Declaring and Managing Dependencies
Gradle provides a rich and flexible model for declaring dependencies, managing versions, and resolving conflicts across builds.
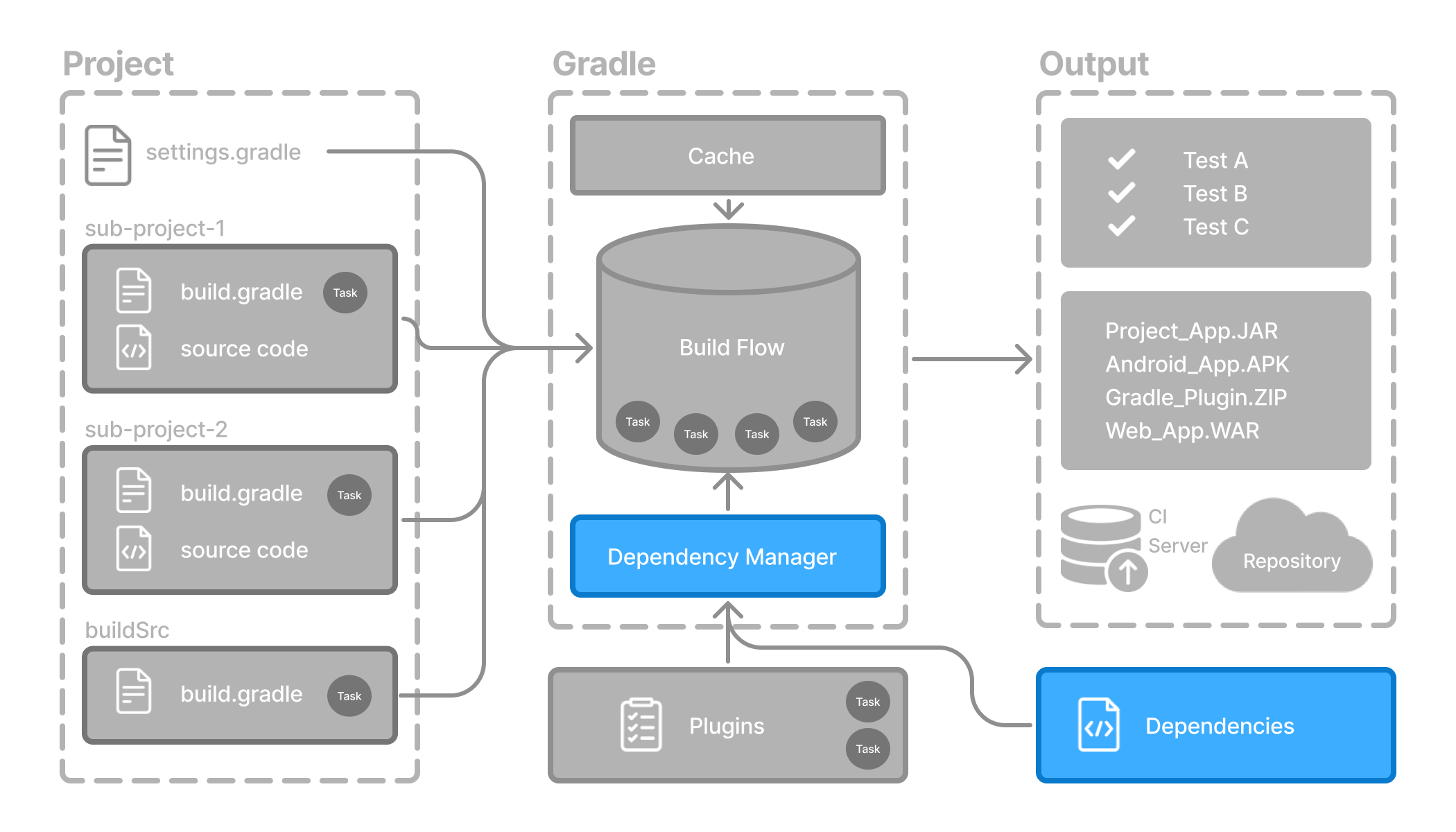
Declare Dependencies
The dependencies{} block is where you declare the external libraries, internal modules, or files your project needs to compile, run, or test:
dependencies {
implementation("com.google.guava:guava:30.0-jre")
runtimeOnly("org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.14.0")
}dependencies {
implementation("com.google.guava:guava:30.0-jre")
runtimeOnly("org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.14.0")
}Each dependency is associated with a configuration, such as implementation, runtimeOnly, or testImplementation, which defines the scope in which it’s used.
Centralize Versions with Version Catalogs
Gradle recommends using version catalogs to declare dependency versions in a single, reusable location:
[versions]
guava = "33.3.1-jre"
junit-jupiter = "5.11.3"
[libraries]
guava = { module = "com.google.guava:guava", version.ref = "guava" }
junit-jupiter = { module = "org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter", version.ref = "junit-jupiter" }You can then use these aliases in your build scripts:
dependencies { (2)
// Use JUnit Jupiter for testing.
testImplementation(libs.junit.jupiter)
testRuntimeOnly("org.junit.platform:junit-platform-launcher")
// This dependency is used by the application.
implementation(libs.guava)
}dependencies { (2)
// Use JUnit Jupiter for testing.
testImplementation libs.junit.jupiter
testRuntimeOnly 'org.junit.platform:junit-platform-launcher'
// This dependency is used by the application.
implementation libs.guava
}Enforce and Constrain Versions
Gradle allows you to constrain dependency versions to avoid unwanted upgrades or enforce known good versions:
dependencies {
implementation("org.apache.httpcomponents:httpclient:4.5.4")
implementation("commons-codec:commons-codec") {
version {
strictly("1.9")
}
}
}dependencies {
implementation("org.apache.httpcomponents:httpclient:4.5.4")
implementation("commons-codec:commons-codec") {
version {
strictly("1.9")
}
}
}You can also constrain a module globally:
dependencies {
implementation("org.apache.httpcomponents:httpclient")
constraints {
implementation("org.apache.httpcomponents:httpclient:4.5.3") {
because("previous versions have a bug impacting this application")
}
implementation("commons-codec:commons-codec:1.11") {
because("version 1.9 pulled from httpclient has bugs affecting this application")
}
}
}dependencies {
implementation 'org.apache.httpcomponents:httpclient'
constraints {
implementation('org.apache.httpcomponents:httpclient:4.5.3') {
because 'previous versions have a bug impacting this application'
}
implementation('commons-codec:commons-codec:1.11') {
because 'version 1.9 pulled from httpclient has bugs affecting this application'
}
}
}Resolve Conflicts with Capabilities
Sometimes multiple libraries provide the same functionality under different coordinates. This can lead to classpath conflicts:
dependencies {
implementation("jaxen:jaxen:1.1.6") // Transitive dependency that brings XPath functionality
implementation("org.jdom:jdom2:2.0.6") // Also offers XPath functionality
}Gradle lets you model these cases using capabilities. For example:
dependencies {
implementation("jaxen:jaxen:1.1.6") {
capabilities {
requireCapability("xml:xpath-support")
}
}
implementation("org.jdom:jdom2:2.0.6")
}Then declare capabilities via a component metadata rule:
components {
withModule("jaxen:jaxen") {
allVariants {
withCapabilities {
addCapability("xml", "xpath-support", "1.0")
}
}
}
withModule("org.jdom:jdom2") {
allVariants {
withCapabilities {
addCapability("xml", "xpath-support", "1.0")
}
}
}
}Gradle will now treat jaxen and jdom2 as alternate implementations and select the one with a required capability.
There are many more ways to influence dependency resolution in Gradle. Consult the Dependency Management chapter to learn more.
Next Step: Learn about Creating and Registering Tasks >>