Binary Plugin Development
When creating a plugin in Gradle, you will most likely offer tasks users can run and DSL blocks that users can use to configure your plugin.
Let’s create a binary plugin that offers both.
When you write a plugin in Gradle, if you want to share it between multiple projects then the best option is to create the plugin in a separate repository. This way, you can publish it to a private or public Maven repository, and then apply it in whatever project you need.
Components of a Plugin
First, let’s review the three components of a plugin:
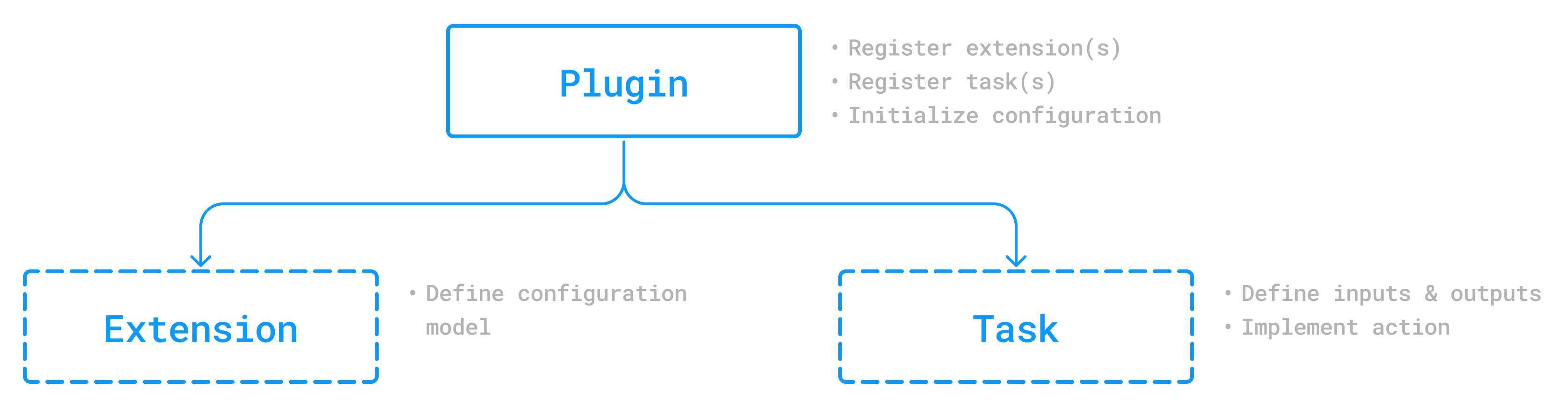
| Component | Role | Description |
|---|---|---|
Plugin Class |
Entry point |
Defines what happens when the plugin is applied. Typically, this involves registering tasks or modifying the project configuration. |
Extension Class |
Configuration |
Holds configuration data provided by users via the build script. |
Task Class |
Behavior |
Implements logic that is executed when the task is run. The plugin will typically register a task and wire it up with values from the extension. |
Our simple plugin compares the size of two files.
It is called FileSizeDiff.
Here’s the suggested directory structure:
.
└── plugin
├── settings.gradle.kts
├── build.gradle.kts
└── src
└── main
└── java/org/example
├── FileSizeDiffTask.java
├── FileSizeDiffPlugin.java
└── FileSizeDiffExtension.java.
└── plugin
├── settings.gradle
├── build.gradle
└── src
└── main
└── java/org/example
├── FileSizeDiffTask.java
├── FileSizeDiffPlugin.java
└── FileSizeDiffExtension.javaThis build.gradle(.kts) for this filesizediff plugin looks as follows:
plugins {
`java-gradle-plugin` (1)
}
group = "org.example" (3)
version = "1.0.0"
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies { (2)
testImplementation("org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.10.0")
testRuntimeOnly("org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine:5.10.0")
testRuntimeOnly("org.junit.platform:junit-platform-launcher")
}
gradlePlugin { (3)
plugins {
create("filesizediff") {
id = "org.example.filesizediff"
implementationClass = "org.example.FileSizeDiffPlugin"
}
}
}plugins {
id('java-gradle-plugin') (1)
}
group = "org.example" (3)
version = "1.0.0"
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies { (2)
testImplementation('org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.10.0')
testRuntimeOnly('org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine:5.10.0')
testRuntimeOnly('org.junit.platform:junit-platform-launcher')
}
gradlePlugin { (3)
plugins {
filesizediff {
id = 'org.example.filesizediff'
implementationClass = 'org.example.FileSizeDiffPlugin'
}
}
}| 1 | java-gradle-plugin - Sets up various configurations you need to do plugin development in Java |
| 2 | junit testing framework - A popular Java testing framework |
| 3 | Plugin configuration - Sets an id of org.example.filesizediff which we can use to reference the plugin |
1. Extension
The extension defines the plugin’s configurable inputs, two file properties in this case:
package org.example;
import org.gradle.api.file.RegularFileProperty;
public interface FileSizeDiffExtension {
RegularFileProperty getFile1();
RegularFileProperty getFile2();
}The two properties representing the input files are of the RegularFileProperty type which extends Property and are therefore lazy.
2. Task
The task does the bulk of the work:
package org.example;
import org.gradle.api.DefaultTask;
import org.gradle.api.file.RegularFileProperty;
import org.gradle.api.provider.Property;
import org.gradle.api.tasks.InputFile;
import org.gradle.api.tasks.OutputFile;
import org.gradle.api.tasks.TaskAction;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public abstract class FileSizeDiffTask extends DefaultTask {
@InputFile
public abstract RegularFileProperty getFile1();
@InputFile
public abstract RegularFileProperty getFile2();
@OutputFile
public abstract RegularFileProperty getResultFile();
@TaskAction
public void diff() throws IOException {
File f1 = getFile1().getAsFile().get();
File f2 = getFile2().getAsFile().get();
String output;
if (f1.length() == f2.length()) {
output = "Files have the same size: " + f1.length() + " bytes";
} else {
String larger = f1.length() > f2.length() ? f1.getName() : f2.getName();
long size = Math.max(f1.length(), f2.length());
output = larger + " was larger: " + size + " bytes";
}
File result = getResultFile().get().getAsFile();
Files.writeString(result.toPath(), output);
System.out.println(output);
System.out.println("Wrote diff result to " + result.getAbsolutePath());
}
}The task defines two input file properties and one output file property:
-
The input files represent the files to compare.
-
The output file is where the plugin writes the diff result, defaulting to
build/diff-result.txt.
The @InputFile and @OutputFile annotations tell Gradle to track these properties for incremental builds and caching, so the task will only re-run if the inputs or outputs change.
The plugin is responsible for mapping the user-defined values from the extension to the task’s input properties.
The task logic is implemented in a method annotated with @TaskAction, which:
-
Compares the size of the two input files.
-
Generates a descriptive text result.
-
Writes that result to the output file and prints it to standard output.
3. Plugin
This class wires up the extension and task when the plugin is applied:
package org.example;
import org.gradle.api.Plugin;
import org.gradle.api.Project;
import org.gradle.api.tasks.TaskProvider;
public class FileSizeDiffPlugin implements Plugin<Project> {
@Override
public void apply(Project project) {
// Register the extension
FileSizeDiffExtension extension = project.getExtensions().create("diff", FileSizeDiffExtension.class);
// Register and configure the task
project.getTasks().register("fileSizeDiff", FileSizeDiffTask.class, task -> {
task.getFile1().convention(extension.getFile1());
task.getFile2().convention(extension.getFile2());
task.getResultFile().convention(project.getLayout().getBuildDirectory().file("diff-result.txt"));
});
}
}In the plugin class, we override the apply method, which is invoked when the plugin is applied to a project via build.gradle(.kts).
Within this method, the plugin does two things:
-
Creates an extension named
filesizediff: This allows users to configure the plugin using adiff {}block in their build script. The configuration values are stored in an instance ofFileSizeDiffExtension. -
Registers a task of type
FileSizeDiffTask: The task is given the namefileSizeDiff, and its properties (file1andfile2) are mapped from the corresponding properties in thediffextension. This ensures the task uses the values provided by the user in their build script.
This enables the following usage in a build.gradle(.kts) file:
plugins {
id("org.example.filesizediff")
}
diff {
file1 = file("a.txt")
file2 = file("b.txt")
}plugins {
id("org.example.filesizediff")
}
diff {
file1 = file('a.txt')
file2 = file('b.txt')
}Next Step: Learn how to test Binary Plugins >>